Whenever you travel with your friends, family, or on a solo trip, milestones by the roadside are something we all came across with. But did you ever notice the uniqueness of milestones? If the answer is yes, then does the same conundrum also arise in your mind, about their colors like Green, Yellow, Orange, Black, Blue, and white)?
The world has changed a lot. And in the 21st century, when we are having the leisure to use the technology called ‘Global Positioning System’, we barely need any kind of help from milestones. But there was a time when Milestones were the most authentic source while traveling. In this article, the writer will explain the reasons behind the different colors of milestones and also the road network of India(As both things are interconnected).
The first traces of road development in the Indian subcontinent can be found in the ancient cities of Harappa and Mohenjodaro of the Indus Valley Civilization around 2800 BC.
But as we all know, with time everything evolves. Like that only, India as a country has also changed a lot. Currently, we have the world's largest road network, with around 62.16 lakh km, second only to the United States of America (Remember, this data changes frequently).Types of Roads-
1- Expressways:-
They are high-speed roads that have four or more lanes and contains modern features like access ramps, grade separation, lane dividers, and elevated section. They are also called “highest class roads in India”. The construction and maintenance work of the Expressway are operated by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MORTH).
2-National Highways-
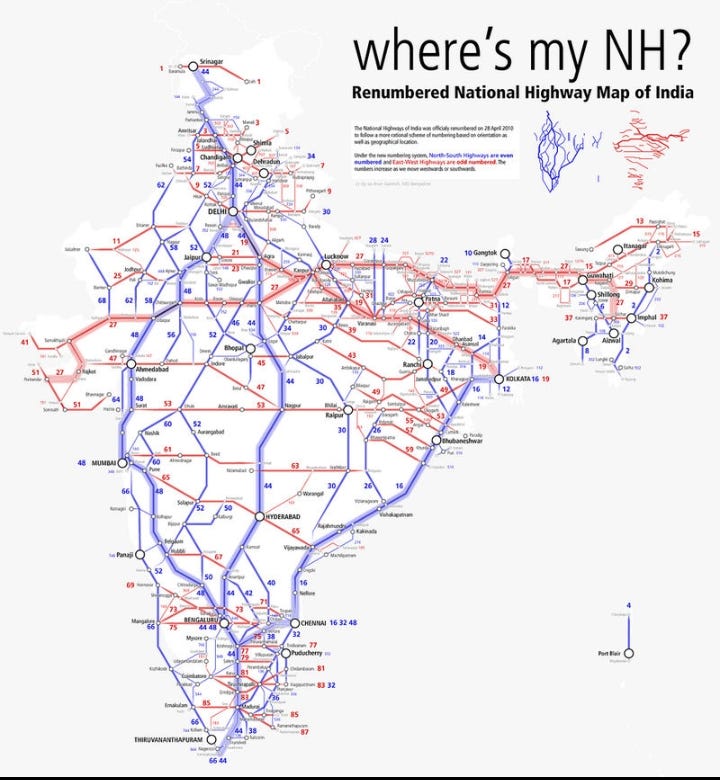
These are the Highways that connect the major cities of India whether it is the capital of states or ports. Also called the “backbone of road infrastructure”. And generally, they have width ranges from 7 m to 15 m.
One most important point to remember, basically in National Highways, north-south corridor (connecting Srinagar to Kanyakumari) has categorized in even numbers like 44, 32, and 52. And East-West corridor (connecting Silchar to Porbandar) are in odd numbers like 27,17 and 43.
3- State Highways-
They are the Highways that mainly connect the major cities throughout the state with National Highways or state highways of neighboring states. They are the roads which have width ranges from 7 m to 10 m.
4-District Roads-
They are the road that connects each district place to the Taluka place. The width of the district roads generally ranges from 5 m to 8 m.
5- Rural Roads-
The roads whichcconnectany village to the district roads is known as Rural roads. The Rural roads are kaccha roads or earthen roads which only carry light traffic.
6-Border Roads-
They are constructed along the northern and northeastern borders of our country. These roads are constructed and maintained by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) which was set up in 1960 by the government of India.
Now you must be thinking, why the writer is playing behind the bushes and not telling us the main point. But trust me, this basic knowledge was very necessary, before you understand the concept of Milestones.
Different colors of Milestones-
1- Yellow Strips-
If you ever see a milestone with this color, that means you are traveling on a National Highway. They integrate different cities and states and cover a length of 1,51,019 km as per statistics in the year 2021. Also, they are maintained by the National Highway Authority.
2- Green Strips-
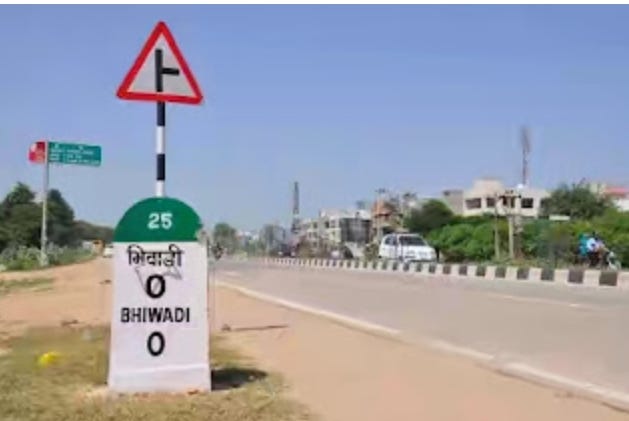
If you see a green color strip on the upper part of the Milestone, that means you are traveling on the State Highway. They connect different cities of a state and span across 176,166 km in length as of data issued in 2016. And is maintained by the State Government.
3- Black/Blue/White Strips-
They signify that you entered a big city or district. There is a 561, 940 km long network of district roads in India at present. And is maintained by the administration of the district.
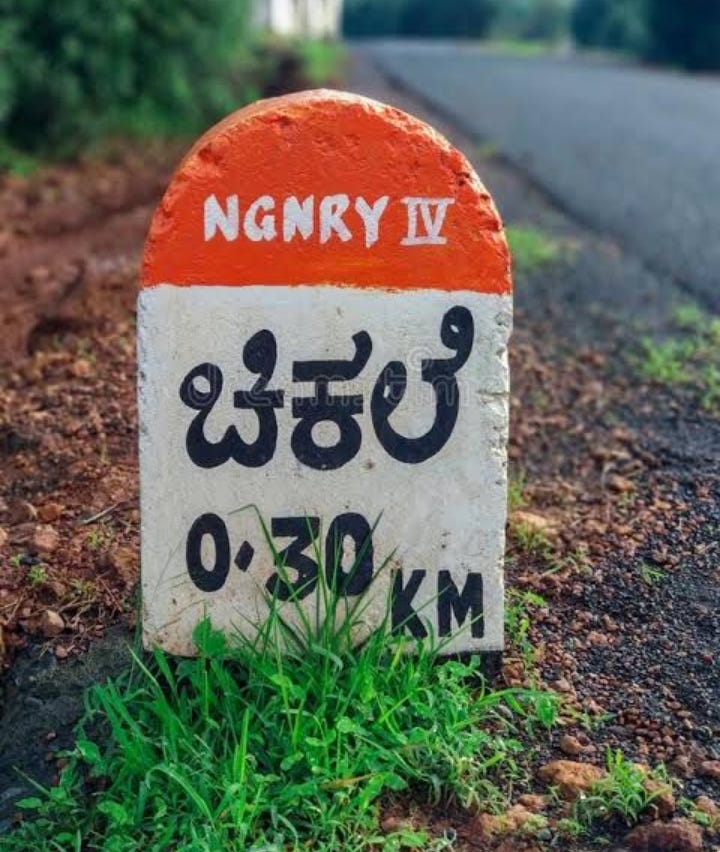
4- Orange Strips-
It shows that you entered the rural area/village. This strip also represents Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana and Jawahar Rozgar Yojna (JRY). Rural roads span across a length of 3.93 lakh km.
What is ‘zero mile center'?
It was the spot used by the British as a reference point to measure the distance of all cities. Nagpur served as the 'zero mile center' and thus served as the geographical center of colonial India. This center has four horses and a sandstone pillar that contains a list giving the exact distance by road to India's major cities.
I hope you learned something new.
Thank you so much for reading!















Very informative Anish. Keep publishing these kinds of articles. Thank you:)
Informative 👍💯